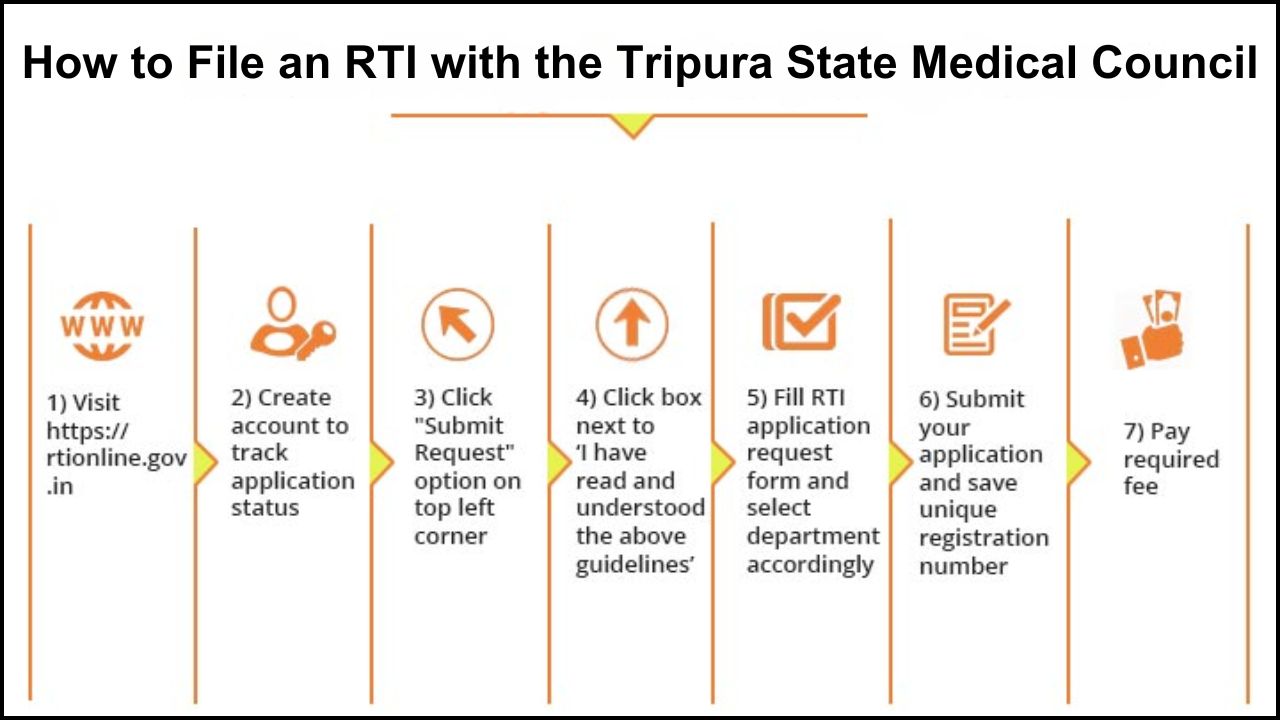
The Tripura State Medical Council (TSMC) plays a crucial role in regulating the medical profession in the state. The council ensures that doctors follow ethical standards and maintain professional conduct. A medical license granted by TSMC allows practitioners to legally serve patients in Tripura. However, the council also holds the authority to cancel licenses under certain circumstances. This article explains the process of license cancellation by TSMC, the specific reasons for which it may occur, and the remedies available to affected medical practitioners.
Table of Contents
Reasons for Medical License Cancellation by TSMC
Misconduct and unethical behavior
- Professional misconduct includes misdiagnosis, overcharging patients, or unethical treatment methods.
- Any action that harms a patient intentionally or due to negligence may lead to license cancellation.
Fake or forged documents submitted during registration
- A doctor registering with fake degrees or experience certificates will face license revocation once detected.
- Verification of academic and professional credentials is strictly followed by TSMC.
Violation of the TSMC code of ethics
- Non-adherence to the medical ethics code laid down by TSMC can result in disciplinary actions.
- Examples include breaching patient confidentiality, advertising unproven treatments, or making false claims.
Criminal conviction involving moral turpitude
- Convictions in criminal cases such as assault, fraud, or harassment may trigger cancellation.
- TSMC may take suo moto action if the practitioner’s behavior is deemed a threat to society.
Practicing without TSMC renewal
- Annual or periodic renewal of the medical license is mandatory.
- Failure to renew or practice with an expired license is considered illegal.
Complaints by patients or healthcare institutions
- Serious complaints supported by evidence may prompt the council to launch an inquiry.
- Based on the investigation, cancellation of the license is possible.
Detailed Reasons and Examples
| Reason | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fraudulent Registration | Submitting fake MBBS or MD certificates to obtain a license | A doctor was found using a forged degree from an unrecognized university |
| Negligence in Treatment | Failing to provide proper care, resulting in patient harm | A case of wrong medication causing death or permanent injury |
| Violation of Ethical Norms | Promoting products for commercial gains or unauthorized practices | Advertising magic cures for chronic diseases on social media |
| Criminal Offenses | Being convicted by a court for crimes involving dishonesty or violence | Conviction in a case of sexual harassment in the workplace |
| Practicing Without Renewal | Continuing medical practice after the license validity ends | A doctor who has not renewed their registration for several years |
| Breach of Patient Confidentiality | Sharing patient details without consent for commercial or personal reasons | Publishing patient photos on social media without consent |
TSMC License Cancellation Process
Complaint Registration or Internal Review
- Any individual or institution can file a complaint with proper documents.
- TSMC may also act on its own after receiving credible information.
Preliminary Scrutiny
- TSMC verifies the complaint to check if it falls within its jurisdiction.
- If valid, the council issues a notice to the medical practitioner.
Inquiry Committee Formation
- A committee is set up to investigate the case.
- The doctor is given a chance to submit a written explanation or appear in person.
Hearing and Evidence Review
- The inquiry committee conducts formal hearings.
- Witnesses and documents are examined during the proceedings.
Final Decision by the Council
- Based on the evidence, the council may issue a warning, suspend, or cancel the license.
- The decision is documented and communicated to the concerned parties.
Notification and Publication
- TSMC updates the official record and notifies relevant hospitals and institutions.
- The cancellation is also published on the official website.
Steps in the TSMC Cancellation Process
| Step | Activity |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Complaint Lodging | Written complaint filed with supporting documents |
| Step 2: Preliminary Review | Council checks whether the issue is under its control |
| Step 3: Show Cause Notice | Notice sent to the doctor for explanation |
| Step 4: Inquiry Committee | The Committee investigates the matter in detail |
| Step 5: Formal Hearing | Opportunity given to defend and present evidence |
| Step 6: Final Decision | Council takes action based on the inquiry outcome |
| Step 7: Official Notification | Information shared with stakeholders and uploaded online |
Remedies Available to the Affected Doctor
Appeal before the State Medical Council Review Board
- Doctors have the right to appeal the decision within a fixed period.
- A review board evaluates whether the cancellation was justified.
Filing a Case in the High Court
- In case of dissatisfaction with the review board, doctors may approach the judiciary.
- A writ petition under Article 226 of the Constitution can be filed.
Providing Additional Evidence
- If new evidence or witnesses can prove the doctor’s innocence, they can be submitted during the appeal.
Request for Reinstatement after Suspension Period
- In some cases, the license is suspended temporarily.
- After the period ends, a reinstatement request can be filed with proof of corrective actions.
Remedy Options for Cancelled Licenses
| Remedy | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Appeal to Review Board | To challenge the cancellation decision within TSMC |
| Legal Recourse in the High Court | To get judicial intervention and a fair hearing |
| Submission of Additional Proof | To provide more documents supporting the doctor’s case |
| Request for Reinstatement | To regain the license after the temporary suspension period ends |
Preventive Measures to Avoid License Cancellation
- Accurate record-keeping ensures transparency and builds trust with patients.
- Following ethical standards helps maintain the dignity of the medical profession.
- Continuous medical education (CME) keeps practitioners updated with best practices.
- Timely renewal of registration avoids legal complications.
- Avoiding false advertisements or exaggerated claims maintains credibility.
- Respecting patient rights and privacy creates a safe treatment environment.
Final Thoughts
A medical license is not only a legal document but a symbol of trust between the doctor and the community. The Tripura State Medical Council has the responsibility to protect patients by ensuring that only qualified and ethical professionals practice medicine. License cancellation is a serious action, taken after careful investigation. However, affected practitioners have remedies and opportunities for defense. By following professional guidelines and ethical principles, doctors can avoid such consequences and continue serving society with dignity.